2025-01-14 15:31:00
ip-vote.com
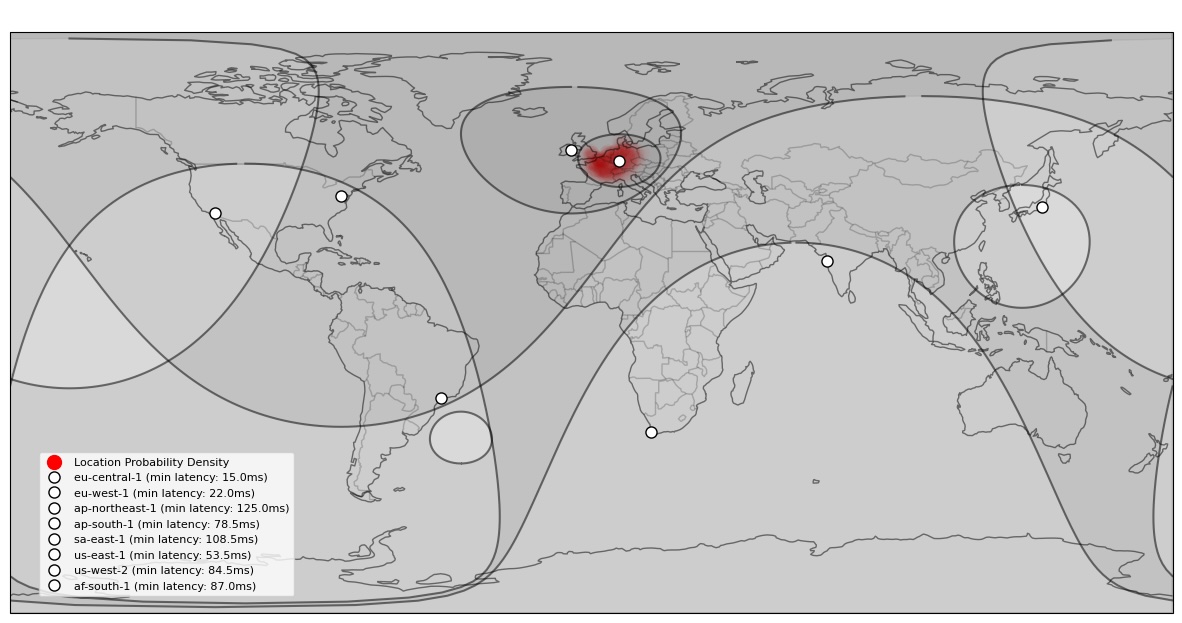
Network Latency Triangulation based Geolocation
Information about a device’s physical location can be inferred by measuring the time it takes for signals to travel between the device and a known server location.
As the speed of light cannot be exceeded according to the known laws of physics, a maximum possible distance can be established with certainty, based on the signal latency.
Multiple measurements to different servers establish circular areas of possible locations on the earth’s surface which can then be intersected.
For more context on how this technology enables reliable online polls, see our article on
IP-based polls as a proxy for popular opinion.
Key Advantages:
- Cannot be manipulated unlike GPS signal derived coordinates, which can be altered by the user’s device before relaying them to the server
- Works even when location services are disabled, provided that the user consents to it’s application
- Can provide supportive evidence for VPN/proxy usage, when the latency is too high for all server locations
How It Works
The process relies on the physical limitations of data transmission through the internet infrastructure:
- Light travels through fiber optic cables at approximately 2/3 the speed of light in vacuum
- Routing inefficiencies and electronics increase the signal latency typically by 20% or more. This range can be represented as a probabilistic distribution.
- The maximum theoretical distance between two points can be calculated based on these limitations and the measured latency
- Multiple measurements to different servers establish circular areas of possible locations on the earth’s surface which can then be intersected
- When trying to alter the apparentlocation, a user can only introduce delays, which will result in a higher location uncertainty but users cannot reduce the network latency beyond the mentioned limits
- Users with a high latency to all servers can be excluded from polls, as this is a strong indicator of a VPN/proxy usage
Application in voting security
Latency-based geolocation can help protect poll integrity by:
- Detecting when poll responses originate from outside the intended geographic region
- Identifying attempts to manipulate polls through elevated VPN/proxy usage
- Providing an additional layer of verification beyond IP-address geolocation and IP-address reputation
Successfully manipulating a poll which employs this method would require following efforts and resources:
- Gaining control over a large number of devices in the target geographic region for submitting votes through those devices
- Alternatively, intercepting and modifying requests at multiple points in the internet routing infrastructure where the servers are connected
- Making sure that the manipulation remains unnoticed
Latency-based geolocation significantly raises the cost of manipulation attempts and can provide very high poll integrity,
if employed in conjunction with other mitigations, such as excluding known data center IP-addresses,
and analysis of response patterns.
Additionally, investigating complaints by potential victims whose IP-address appears to have been
already used for voting on a poll unbeknownst to them, can help to uncover manipulation attempts.
More about this project:
Technical Implementation
In our implementation, we added a few additional parts to make it work:
- As the clocks of the computers of the client and the servers may not be synchronized, we first approximate the clock difference among the clocks (using the Network Time Protocol algorithm).
This clock difference may be imperceptibly short for humans but may nonetheless be significant for the latency measurement. - To mitigate certain manipulation attempts, the master server first generates a random number and sends it to the client’s device, which relays it to the latency measurement servers.
This prevents the client sending latency measurement requests ahead of time, which would allow them to pretend to be closer to a server than they actually are. - Before measuring latencies, the client’s device sends requests to all servers to already establish HTTPS sessions.
Creating a HTTPS session requires multiple network roundtrips and therefore considerable time and would add unnecessary noise to the actual latency measurements.

Signal transmission outside the internet infrastructure
In the above described location inference, the reduced speed of light inside glass fibers is assumed, which is 2/3 that of the speed of light in vacuum or air.
Therefore sending signals through the atmosphere or space may enable the manipulation of the apparent location to some degree.
One conceivable approach might be to use long range radio signals travelling through the atmosphere over large distances.
And another approach might be to use SpaceX’s Starlink satellite infrastructure. Both could potentially be used to distribute the random number faster than using the conventional internet infrastructure.
However, the complete exploitation of this approach would also require spoofing the IP-addresses of the distributed devices participating in the concerted manipulation attempt to appear as a single device.
The use of HTTPS would further complicate the realisation of this manipulation approach. Nonetheless, with significant effort, it may be possible to alter the apparent location.
A successful manipulation following this approach may however only shift the apparent location to a certain degree, as the speed of light in glass fibers is in the same order of magnitude as the speed of light in air or vacuum.
Looking at further implementation hurdles, Starlink’s satellites are typically in ~500 km altitude which slows the
signal for short distances on the surface. Similarly the generation and reception of radio signals would likewise introduce additional latencies, which
would require significant engineering efforts to be compensated for.
And finally, for the successful manipulation of a significant poll, this approach would need to be applied to a large number of votes without being noticed.
Considering the necessary resources and effort required, the manipulation approaches seem impractical for most polls, even if they carry a relatively high degree of societal impact and incentives for manipulation.
Conclusion
Network latency triangulation based geolocation is a method to determine the physical location of a device with a high degree of confidence.
It can be used to detect when poll responses originate from outside the intended geographic region, and to provide an additional layer of verification beyond IP-address geolocation and IP-address reputation.
For poll outcomes to be truly reliable, location measurements should be performed by multiple independent audited entities.
Keep your files stored safely and securely with the SanDisk 2TB Extreme Portable SSD. With over 69,505 ratings and an impressive 4.6 out of 5 stars, this product has been purchased over 8K+ times in the past month. At only $129.99, this Amazon’s Choice product is a must-have for secure file storage.
Help keep private content private with the included password protection featuring 256-bit AES hardware encryption. Order now for just $129.99 on Amazon!
Support Techcratic
If you find value in Techcratic’s insights and articles, consider supporting us with Bitcoin. Your support helps me, as a solo operator, continue delivering high-quality content while managing all the technical aspects, from server maintenance to blog writing, future updates, and improvements. Support Innovation! Thank you.
Bitcoin Address:
bc1qlszw7elx2qahjwvaryh0tkgg8y68enw30gpvge
Please verify this address before sending funds.
Bitcoin QR Code
Simply scan the QR code below to support Techcratic.

Please read the Privacy and Security Disclaimer on how Techcratic handles your support.
Disclaimer: As an Amazon Associate, Techcratic may earn from qualifying purchases.